目录
记一次与bucket table相关的小文件问题,百万级小文件。
前言
最近遇到了一次跟Spark bucket table相关的小文件问题。
场景如下:
存在一张bucket table, bucket column 是 c1, bucket数量是1000,用户在对这张bucket 表进行insert overwrite的时候,已经将spark.sql.shuffle.partitions 设置成了1000,而且对bucket column那列进行了distribute by 操作,理想情况下,这次overwrite操作将生成1000个文件,但是出人意料的是,这次操作生成了 1000*1000=100万个小文件!!!
这么多小文件必定需要很多次create 请求和rename请求,因此必然的触发了Hadoop集群报警机制。
关于Bucket Table
Spark和Hive中都有bucket table,但是其格式不尽相同。本文不对此进行赘述,关于内容是关于Spark的bucket表。
Bucket表的作用相当于一种数据预处理,如果两个bucket 表的bucket数量相同,且对两个表的bucket key进行join,那个可以避免shuffle 操作,需要数据管理者进行一定的设计。
创建bucket 表
语句格式:
CREATE TABLE [IF NOT EXISTS] [db_name.]table_name
[(col_name1 col_type1 [COMMENT col_comment1], ...)]
USING data_source
[OPTIONS (key1=val1, key2=val2, ...)]
[PARTITIONED BY (col_name1, col_name2, ...)]
[CLUSTERED BY (col_name3, col_name4, ...) SORTED BY (col_name1 ASC, col_name2 DESC) INTO num_buckets BUCKETS]
[LOCATION path]
[COMMENT table_comment]
[TBLPROPERTIES (key1=val1, key2=val2, ...)]
[AS select_statement]
PS: 创建bucket表时候用到的clustered by (key) 和 sorted by (key),和在select 数据时候用的cluster by key 和sort by key 很相似,但是用法是不同的。
另外在select 时候有distribute by 和 cluster by两种语法,cluster by key = distribute by key sort by key. distribute by key = hash shuffle by key.
Bucket表参数
Spark中有两个bucket表相关参数:
spark.sql.sources.bucketing.enabled 是否将bucekt表看成是bucekt表
spark.sql.sources.bucketing.maxBuckets 允许的最大bucekt 数量,默认是100000
关于第一个参数,作用是否将bucket表看成是bucekt表。
Spark针对bucket表读取的时候,会对每一个bucket分配一个task来读取,因为如果进行bucket join就不能再对这个bucket的数据进行拆分。但是有些时候,我们不是读取这个bucket表进行join,比如是简单的ETL,而此时map阶段会针对每个bucket分配一个mapTask,而如果这个bucket数据量很大,就会很缓慢。而如果此时,我们把spark.sql.sources.bucketing.enabled 设为false,那么就相当于一个普通表,map端可能会针对这个bucket的数据进行split,从而多分配一些task,加快速度。
Insert into bucket table
Insert into bucket table的时候,会加一个针对bucket column的hashPartitioning 函数。因此如果一个task中的数据在insert into这个bucket table的时候,没有提前针对这个bucket column 进行过基于bucket number 的hash(可以将spark.sql.shuffle.partitions 设置为bucket number,然后进行distribute/cluster by),那么每个task 将会生成 bucket number个文件。
问题分析
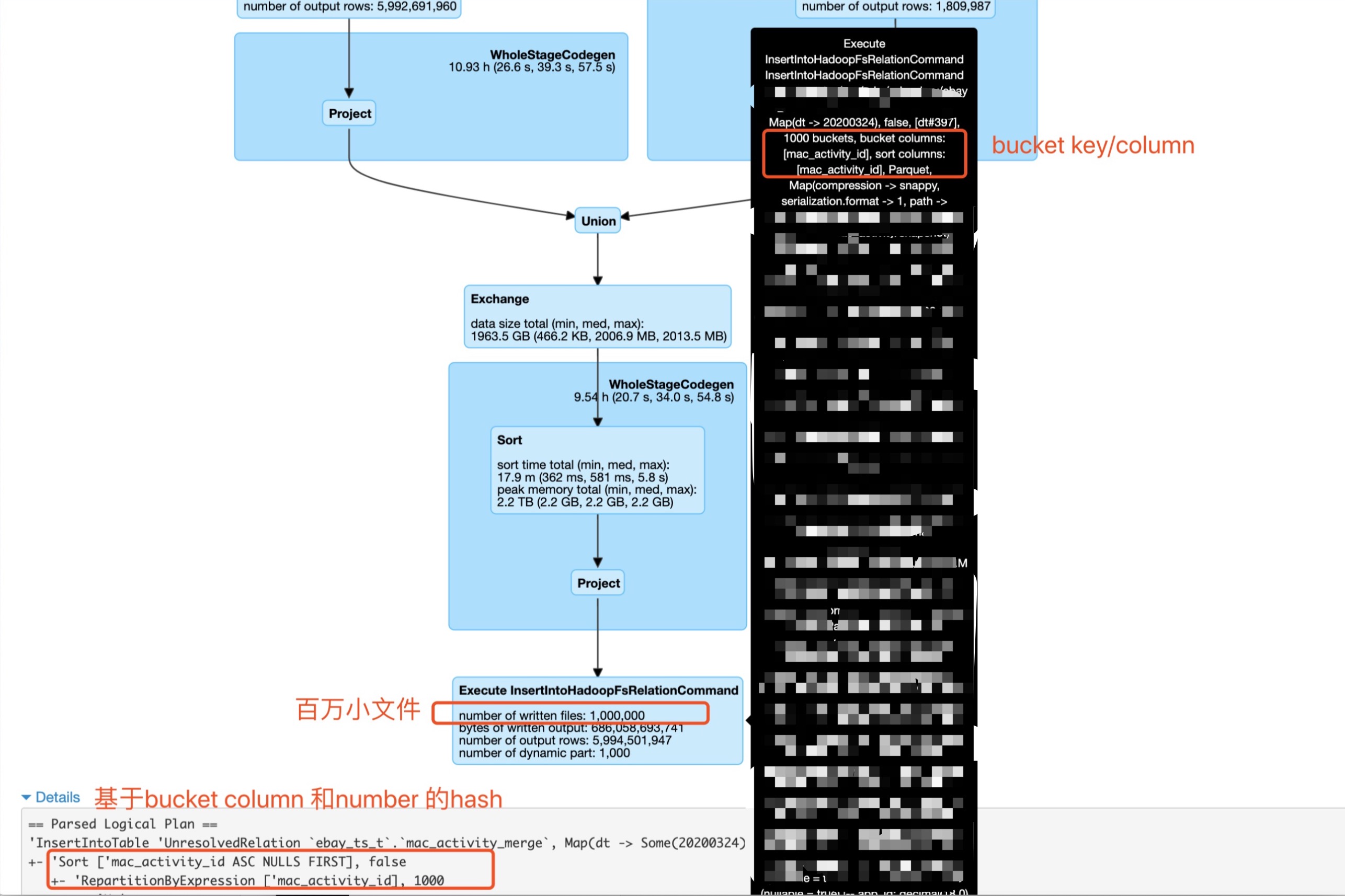
出现问题的sql语句的执行计划核心部分如下图所示。
可以看到这是对两个子查询进行union,然后我们做了基于bucket column和number的hash(distribute and sort by), 之后insert overwrite 一个bucekt表。
用户期望的结果是会最终产生1000个文件,但是出乎意料的生成了100万个小文件。
通过对语句进行精简,我拿到一个可复现问题的简单测试。
sql(s"create table ta (c1 decimal(38, 18), c2 int, p1 int) using parquet partitioned" +
" by (p1) clustered by (c1) sorted by (c1) into 10 buckets")
sql("set spark.sql.shuffle.partitions=10")
spark.sparkContext.parallelize(Seq.range(1, 1000), 1000)
.map(v => (Decimal(v), v)).toDF("c1", "c2").write.mode("overwrite")
.saveAsTable("tb")
spark.sparkContext.parallelize(Seq.range(1, 1000), 1000)
.map(v => (v.toDouble, v)).toDF("c1", "c2").write.mode("overwrite")
.saveAsTable("tc")
sql("insert overwrite table ta partition(p1=1) select c1, c2 from tb union all " +
"select c1, c2 from tc distribute by c1")
在这个测试中有三张表,ta是一张bucket表,有三列, c1, c2, p1, 而p1是分区列,c1是bucket列, bucket 数目是10. 我们已经将spark.sql.shuffle.partitions 设置为10.
然后tb 和tc都有两列 c1, c2, 我们将select 两张表的数据,进行union,之后对c1 进行distribute by,之后overwrite 到 ta 中p1=1的分区。
执行之后,查看ta下面p1=1目录,发现有200个小文件(已经很多了)。
查看insert overwrite语句物理执行计划。
== Physical Plan ==
Execute InsertIntoHadoopFsRelationCommand file:/private/var/folders/lw/8qtm67pn1gdb86hj4jcrk_ww39cyt7/T/spark-40631839-0276-414f-aa2f-0721eaab3e26, Map(p1 -> 1), false, [p1#255], 10 buckets, bucket columns: [c1], sort columns: [c1], Parquet, Map(path -> file:/private/var/folders/lw/8qtm67pn1gdb86hj4jcrk_ww39cyt7/T/spark-40631839-0276-414f-aa2f-0721eaab3e26), Overwrite, CatalogTable(
Database: default
Table: ta
Created Time: Sat Mar 28 10:19:48 PDT 2020
Last Access: UNKNOWN
Created By: Spark 3.1.0-SNAPSHOT
Type: EXTERNAL
Provider: parquet
Num Buckets: 10
Bucket Columns: [`c1`]
Sort Columns: [`c1`]
Location: file:///private/var/folders/lw/8qtm67pn1gdb86hj4jcrk_ww39cyt7/T/spark-40631839-0276-414f-aa2f-0721eaab3e26
Partition Provider: Catalog
Partition Columns: [`p1`]
Schema: root
|-- c1: decimal(38,18) (nullable = true)
|-- c2: integer (nullable = true)
|-- p1: integer (nullable = true)
), org.apache.spark.sql.execution.datasources.CatalogFileIndex@3faae831, [c1, c2, p1]
+- *(3) Project [ansi_cast(c1#250 as decimal(38,18)) AS c1#254, c2#247, 1 AS p1#255]
+- Exchange hashpartitioning(c1#250, 10), false, [id=#155]
+- Union
:- *(1) Project [cast(c1#246 as double) AS c1#250, c2#247]
: +- *(1) ColumnarToRow
: +- FileScan parquet default.tb[c1#246,c2#247] Batched: true, DataFilters: [], Format: Parquet, Location: InMemoryFileIndex[file:/Users/fwang12/todo/apache-spark/sql/core/spark-warehouse/org.apache.spark..., PartitionFilters: [], PushedFilters: [], ReadSchema: struct<c1:decimal(38,18),c2:int>
+- *(2) ColumnarToRow
+- FileScan parquet default.tc[c1#248,c2#249] Batched: true, DataFilters: [], Format: Parquet, Location: InMemoryFileIndex[file:/Users/fwang12/todo/apache-spark/sql/core/spark-warehouse/org.apache.spark..., PartitionFilters: [], PushedFilters: [], ReadSchema: struct<c1:double,c2:int>
原来虽然表tb 和tc中都有名为c1的列,但是一个是Decimal类型,一个是double类型。在做union的时候,取 double 和Decimal的公共类型double,因此对表tb中的c1 进行了cast(c1 as double),但是在insert overwrite bucket table的时候,由于bucket column c1的类型是Decimal,所以我们可以看到在进行Exchange hashpartitioning 之后进行了Project [ansi_cast(c1#250 as decimal(38,18)) AS c1#254, c2#247, 1 AS p1#255] 操作,又把double转成了Decimal.
因此,我们前面hash 后的数据是基于double类型的hash,而bucket column类型是Decimal类型。
查看FileFormatWriter中的write方法,其逻辑为,如果currentPartitionValue或者currentBucketId与next 不同。
那么会创建一个新的文件。
if (currentPartionValues != nextPartitionValues || currentBucketId != nextBucketId) {
// See a new partition or bucket - write to a new partition dir (or a new bucket file).
if (isPartitioned && currentPartionValues != nextPartitionValues) {
currentPartionValues = Some(nextPartitionValues.get.copy())
statsTrackers.foreach(_.newPartition(currentPartionValues.get))
}
if (isBucketed) {
currentBucketId = nextBucketId
statsTrackers.foreach(_.newBucket(currentBucketId.get))
}
fileCounter = 0
newOutputWriter(currentPartionValues, currentBucketId)
}
而double类型和Decimal类型getBucketId的算法是不同的。
具体的实现涉及到org.apache.spark.sql.catalyst.expressions.InterpretedHashFunction类中的hash方法。可以看到double类型和decimal类型有不同的实现。
所以对double类型值其计算得到值和转化为Decimal再计算时不同的,附录中也提供了实践的验证方法。
/**
* Computes hash of a given `value` of type `dataType`. The caller needs to check the validity
* of input `value`.
*/
def hash(value: Any, dataType: DataType, seed: Long): Long = {
value match {
case null => seed
case b: Boolean => hashInt(if (b) 1 else 0, seed)
case b: Byte => hashInt(b, seed)
case s: Short => hashInt(s, seed)
case i: Int => hashInt(i, seed)
case l: Long => hashLong(l, seed)
case f: Float => hashInt(java.lang.Float.floatToIntBits(f), seed)
case d: Double => hashLong(java.lang.Double.doubleToLongBits(d), seed)
case d: Decimal =>
val precision = dataType.asInstanceOf[DecimalType].precision
if (precision <= Decimal.MAX_LONG_DIGITS) {
hashLong(d.toUnscaledLong, seed)
} else {
val bytes = d.toJavaBigDecimal.unscaledValue().toByteArray
hashUnsafeBytes(bytes, Platform.BYTE_ARRAY_OFFSET, bytes.length, seed)
}
...
}
因此,hash后的double类型数据,在转为Decimal之后,虽然其partitionValue获取是一致的,但是bucketId获取方法存在差异,因此一个task依然生成了十个bucket文件,造成了小文件的爆炸。
关于double 和Decimal
除此之外,此处在简单介绍下double 和Decimal。
double是一种采用科学计数法进行表示的模糊类型,其增大了表示范围,但是却丢失了表示精度。详细可参考前面写的一篇文章重新了解数字类型。
而且前面提到的用户union 两个子查询,子查询有同名的列,一列是double, 一列是Decimal,而且以这两列进行Join key 进行join。
double是一个模糊类型, Decimal是一个精确类型,在Spark中比较double 和Decimal的时候会将Decimal转化为double(强制类型转化) 然后与double进行比较,而这种比较是不精确的,容易造成输出爆炸。
因此慎用double类型作为join key。
例如下面的两个double 是不同的数字,比较相等却是true。
scala> 112345678901234568d == 112345678901234560d
res0: Boolean = true
解决方案
解决问题,可以从三方面考虑。
- 绕过这个数字类型,解决小文件问题
- 通过重建表从根本解决问题
- 平台侧可以做什么
绕过数字类型,解决小文件问题
有两种方案。
第一种是用一个中间过渡表
首先将两个子查询 union之后的数据,写入到中间表。然后再select 这个中间表,然后对bucket column 对应的列进行cluster by(spark.sql.shuffle.partitions需要与bucket numer相同).
这种方法的缺点是引入了working表,优点是可以分别针对 写入中间表部分和写入bucket表部分设置合适的spark.sql.shuffle.partitions.
第二种方法是修改sql语句
修改前:
insert overwrite table ta partition(p1=1) select c1, c2 from tb union all select c1, c2 from tc distribute by c1
修改后:
set spark.sql.shuffle.partitions=10 // bucket number
insert overwrite table ta partition(p1=1) select cast(c1 as Decimal(38, 18)) as c1, c2 from (select c1, c2 from tb union all select c1, c2 from tc) tmp distribute by c1
我们修改了语句,手动的将union之后为double类型c1 转为Decimal类型,然后再针对Decimal 类型的bucket 列进行 distributed by操作。当然在此之前,我们要将spark.sql.shuffle.partitions设为与bucket number相同的值。
通过重建表从根本解决问题
强烈推荐用户使用这种方案。
平台侧可以做什么
在上面我们提到了我们的distribute/cluster是针对 union子查询的数据进行的,而在此之后要插入bucket表,又进行了类型转换。
所以,平台是否可以针对insert bucket table这种case,做类似于谓词下推的把CAST下推到 distribute/cluster by 之前?
后记
如果是一万个bucket 的bucket表,那岂不是小文件要破亿了?
附录
验证double 和Decimal 类型的bucket Id 是否不同
此处使用json格式是因为其可以直接查看数据。
在跑完之后去查看表下面的文件,文件名格式:
part-{partId}-{UUID}_{bucketId}.c000.json
我们只需对比两张表同样bucketId 文件下面的内容不同即可得出结论。
sql("create table ta(c1 double, c2 int) using json clustered by(c1) into 10 buckets")
sql("create table tb(c1 decimal(38, 18), c2 int) using json clustered by (c1) into 10 buckets")
sql("create table tc(c1 double, c2 int) using json")
sql("create table td(c1 decimal(38, 18), c2 int) using json")
sql("insert into tc select * from values(1,1),(2,2),(3,3),(4,4),(5,5),(6,6),(7,7),(8,8),(9,9), (10, 10)")
sql("insert into td select * from values(1,1),(2,2),(3,3),(4,4),(5,5),(6,6),(7,7),(8,8),(9,9),(10,10)")
sql("insert overwrite table ta select * from tc")
sql("insert overwrite table tb select * from td")